Storage & Shelf Life Prediction for Flange Gasket Materials
By Laverne Fernandez
FSA Member, Garlock Sealing Technologies
Flange gaskets are highly engineered products, and their performance depends on many factors. Certainly design, manufacture, installation, and process conditions are all critical, but so is storage before use. Gasket materials often remain in storage for a long time before they are placed into service. Unfortunately, storage practices for gasket materials are generally not optimal or controlled well enough. This article provides guidance for the storage of different gasket materials to preserve their integrity. Gasket materials are divided into three main categories: non-metallic, semi-metallic and metallic. Non-metallic gaskets, or soft gaskets, are fabricated from materials such as rubber, fiber, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and graphite. The material properties make them ideal for flat-faced applications with low pressures. Metallic gaskets are fabricated from one or a combination of metals. Semimetallic gaskets are composed of metal and non-metallic materials. The metal is intended to offer strength and resilience while the non-metallic components provide conformability and sealabililty. These types of gasket are used in higher-pressure applications.
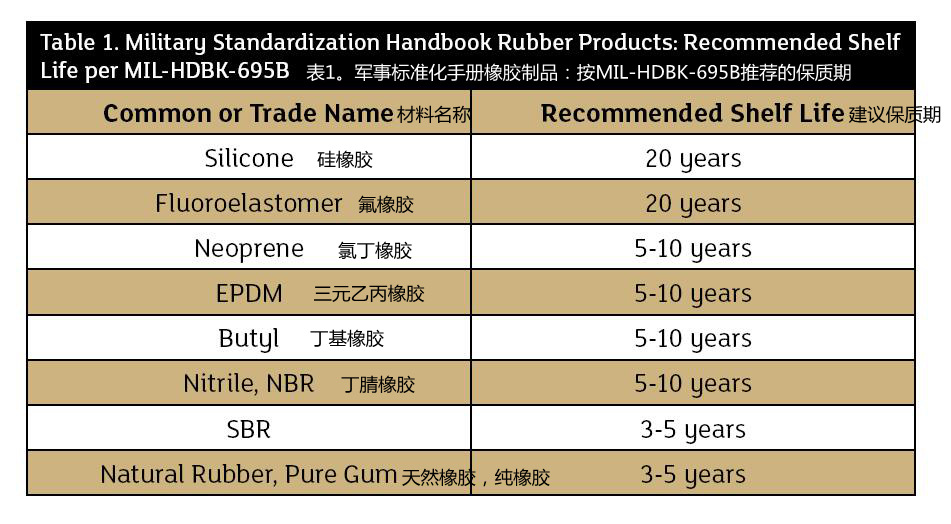
The most common semi-metallic gaskets are spiral wound gaskets. Shelf life is defined as the period of time during which a material may remain suitable for use during storage. While shelf life is a term generally discussed with regard to storage and not service life, it is important to note that storage conditions can affect service life. Shelf life varies depending on product specifications and compound design. Gasket materials typically remain in storage for several months before they are used. Therefore, shelf life is an important consideration for the end user. Gasket degradation can be the result of a combination of factors such as oxygen, ozone, light, heat, humidity, oils, water, solvents, acids and vapors. The Impact of Component Material Materials with elastomeric binders will inevitably deteriorate over
 time. These gasket materials are widely used in many industries and have proven to provide reliable service in bolted flange connections. Elastomer-bonded fiber materials can be made of complex materials. The principal components include a rubber (elastomer) binder, reinforcing fibers and filler components. The aging process of these types of gaskets involves an irreversible chemical process, and they are very susceptible to deterioration from higher ambient temperatures. Degradation is also typically accelerated by direct sunlight. The reinforcing fibers are often considered the most stable of the components, but modern fibers do gradually dry out, weather and deteriorate. Filler components are often the greatest contributor to gasket deterioration. These components come in many forms from many different chemical families and are generally unique to every manufacturer. They are selected and combined to optimize gasket performance. The speed in which this process takes place is highly dependent on the material composition along with its quality and storage conditions. There are gasket materials, however, that are essentially inert and unaffected by extended storage periods. For graphite and PTFE gaskets that contain no binders, sheets and gaskets of these materials have a virtually indefinite shelf life. In the case of metallic and semimetallic gaskets with graphite or PTFE soft material, the theoretical shelf life is infinite in ideal conditions. However, in reality excessive dust could cause compatibility issues with the process, while exposure to humidity and moisture can cause oxidation of the metal components. Poor storage environments can lead to premature reduction in quality, especially when conditions of elevated temperature, inappropriate humidity levels and strong light exist. Optimum storage conditions are defined as: ? Temperature range: between 40 degrees Fahrenheit [F] (5 degrees Celsius [C]) and 80 F (25 C) o Storage of gaskets in freezing conditions is not recommended. While exposure to freezing temperatures may not permanently damage the gasket, it should be allowed to warm to room temperature conditions before being placed into service. ? Relative humidity: 40 to 75 percent o Condensation should not be allowed to occur. ? Light: Darkened storeroom o Non-ultraviolet (UV) or low-UV producing lights ? Minimal dust content and the absence of chemicals stored in proximity Without getting into the details of the multitude of variables that affect
time. These gasket materials are widely used in many industries and have proven to provide reliable service in bolted flange connections. Elastomer-bonded fiber materials can be made of complex materials. The principal components include a rubber (elastomer) binder, reinforcing fibers and filler components. The aging process of these types of gaskets involves an irreversible chemical process, and they are very susceptible to deterioration from higher ambient temperatures. Degradation is also typically accelerated by direct sunlight. The reinforcing fibers are often considered the most stable of the components, but modern fibers do gradually dry out, weather and deteriorate. Filler components are often the greatest contributor to gasket deterioration. These components come in many forms from many different chemical families and are generally unique to every manufacturer. They are selected and combined to optimize gasket performance. The speed in which this process takes place is highly dependent on the material composition along with its quality and storage conditions. There are gasket materials, however, that are essentially inert and unaffected by extended storage periods. For graphite and PTFE gaskets that contain no binders, sheets and gaskets of these materials have a virtually indefinite shelf life. In the case of metallic and semimetallic gaskets with graphite or PTFE soft material, the theoretical shelf life is infinite in ideal conditions. However, in reality excessive dust could cause compatibility issues with the process, while exposure to humidity and moisture can cause oxidation of the metal components. Poor storage environments can lead to premature reduction in quality, especially when conditions of elevated temperature, inappropriate humidity levels and strong light exist. Optimum storage conditions are defined as: ? Temperature range: between 40 degrees Fahrenheit [F] (5 degrees Celsius [C]) and 80 F (25 C) o Storage of gaskets in freezing conditions is not recommended. While exposure to freezing temperatures may not permanently damage the gasket, it should be allowed to warm to room temperature conditions before being placed into service. ? Relative humidity: 40 to 75 percent o Condensation should not be allowed to occur. ? Light: Darkened storeroom o Non-ultraviolet (UV) or low-UV producing lights ? Minimal dust content and the absence of chemicals stored in proximity Without getting into the details of the multitude of variables that affect
